WHAT IS CNC ROUTING/MACHINING?
You first you need to understand what a router is:
A Router is a tool that is used to rout out (hollow out) a desired area in a solid material.
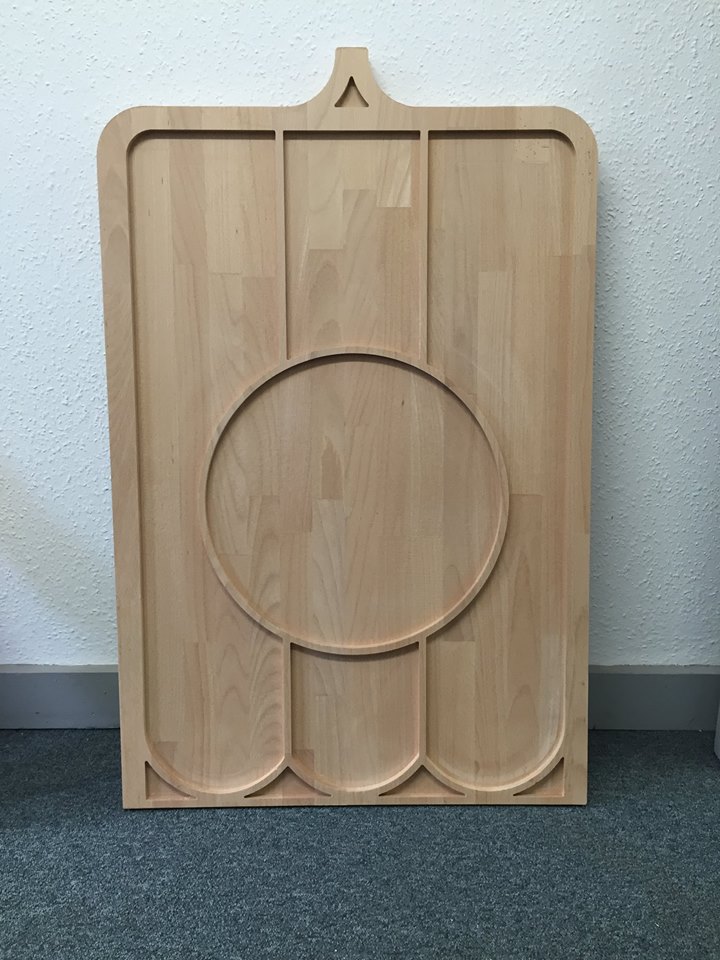

Here you can see where a section of wood has been hollowed out using a router.
A CNC router is essentially a router that is controlled by a computer. As mentioned in my basic post on CNC routing, CNC stands for computer numerical control.
A CNC router can easily produce a rapid prototype one off, or just effectively a large array of repetitive component parts. The main benefits from a CNC router are Automation and precision. A CNC machine can produce complex shapes and parts that would be near on impossible to create manually.
An example CNC router for reference and to show the bed size of 8-4ft.
CNC routers are manufactured with different size beds (working surface) to suit the material size you will be routing.
Typical 3 axis CNC routers are either 5 x 5ft, 4 x 8ft, and 5 x 10ft.
The CNC router itself is controlled by motors. The usual components that make up a CNC router are one or more spindle motors, servo motors, Stepper Motors, servo amplifiers, AC inverter frequency drives, linear guides and ball screws.
CNC routers work on the Cartesian coordinate system of three axis (X, Y, Z) for 3D motion control.
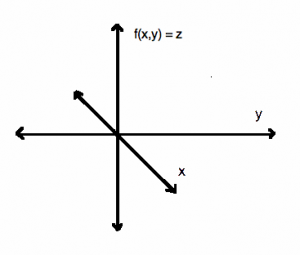
CNC – Three Axis – Cartesian graph
CNC machines are controlled via a language called G-code.
First a drawing of the model is created within CAD software and then is converted into G-code so that the machine can understand the coordinates of the design, feed rate, location and speeds.

Here is a photo of our CNC machine routing a part from plywood. This was designed in CAD and then exported as G-code toolpaths for the CNC machine to read the data.
I hope this has provided you with a better understanding of what CNC routing/machining actually is.